
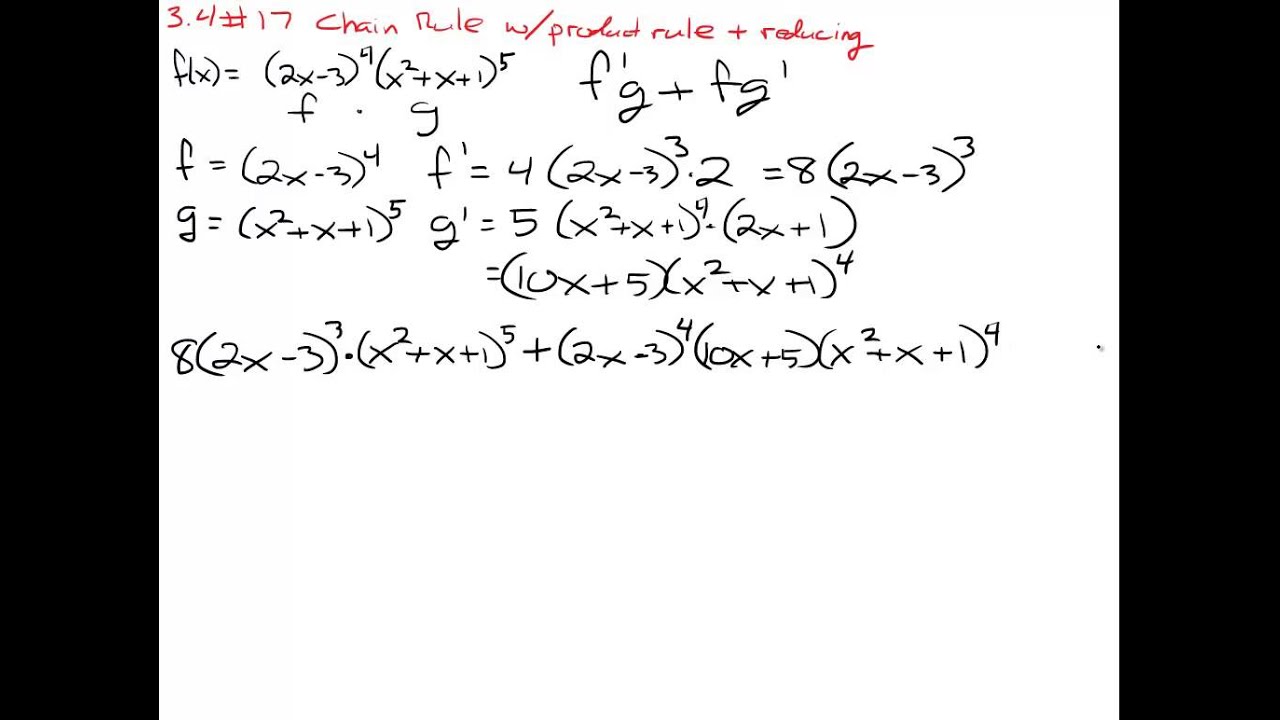
Ĭlick HERE to see a detailed solution to problem 21.Ĭlick HERE to return to the original list of various types of calculus problems. With tangent lines parallel to the line y + x = 12. PROBLEM 21 : Find all points ( x, y) on the graph of.


The product rule is a formal rule for differentiating problems where one function is multiplied by another. In the following discussion and solutions the derivative of a function h( x) will be denoted by or h'( x). There is also an excellent Calc III review sheet made by a friend of mine from the University of Connecticut, which I have also included here.The following problems require the use of the product rule. The content is based on MATH 13 at Tufts University and follows closely the text of Calculus – Early Transcendentals by Briggs and Cochran.Ĭhapter 11 – Vectors and Vector-Valued Functionsġ1.1 – Vectors in the Plane, 11.2 – Vectors in Three Dimensions, 11.3 – Dot Products, 11.4 – Cross Products, 11.5 – Lines and Curves in Space, 11.6 – Calculus of Vector-Valued Functions, 11.7 – Motion in Space, and 11.8 – Length of CurvesĬhapter 12 – Functions of Several Variablesġ2.1 – Planes and Surfaces, 12.2 – Graphs and Level Curves, 12.4 – Partial Derivatives, 12.5 – The Chain Rule, 12.6 – Directional Derivatives and the Gradient, 12.7 – Tangent Planes and Linear Approximations, 12.8 – Maximum/Minimum Problems, 12.9 – Lagrange Multipliersġ3.1 – Double Integrals over Rectangular Regions, 13.2 – Double Integrals over General Regions, 13.3 – Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates, 13.4 – Triple Integrals, 13.5 – Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinatesġ4.1 – Vector Fields and Integrals, 14.2 – Line Integrals, 14.3 – Conservative FieldsĬhapter 14, Part II – Vector Calculus – Part IIġ4.4 – Green’s Theorem, 14.5 – Divergence and Curl, 14.6 – Surface Integrals, 14.7 – Stokes’ Theorem, 14.8 – Divergence Theorem The links below contain review material for an undergraduate-level course on multivariable calculus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
